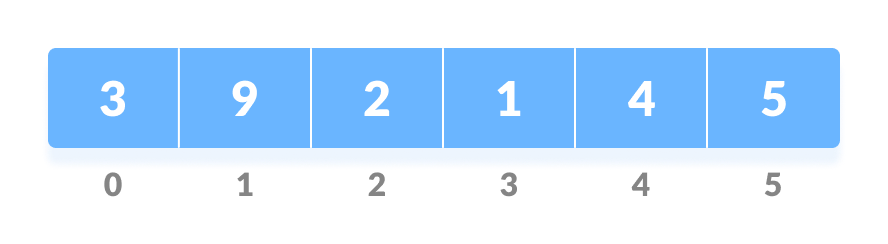
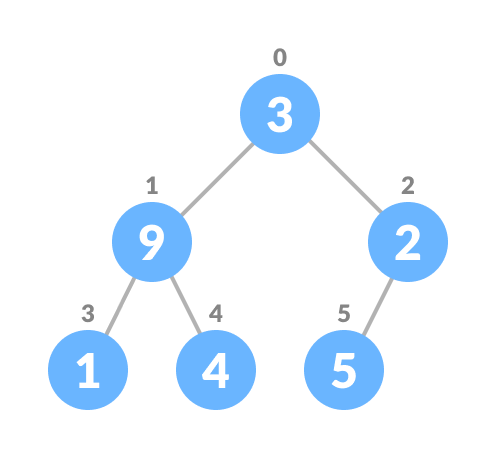
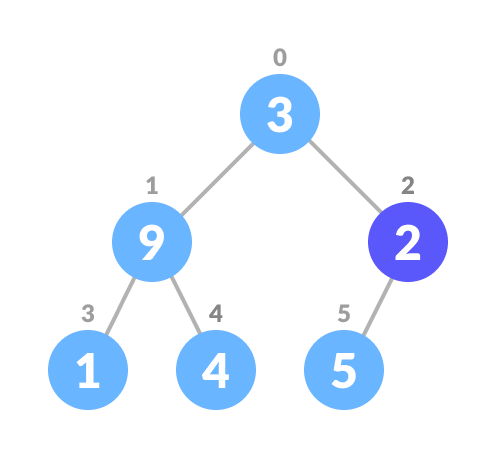
If leftChild is greater than currentElement (i.e. element at ith index), set leftChildIndex as largest.
If rightChild is greater than element in largest , set rightChildIndex as largest .
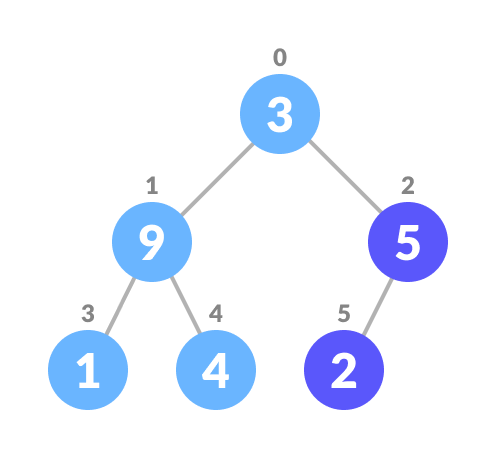
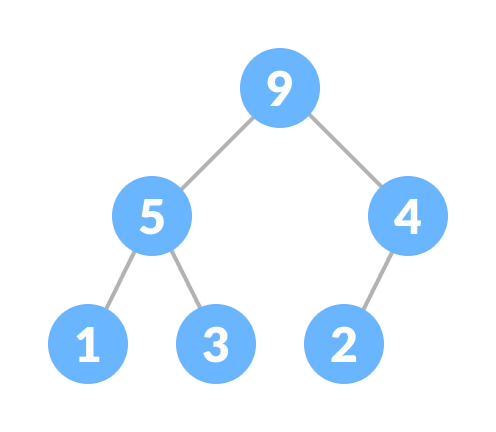
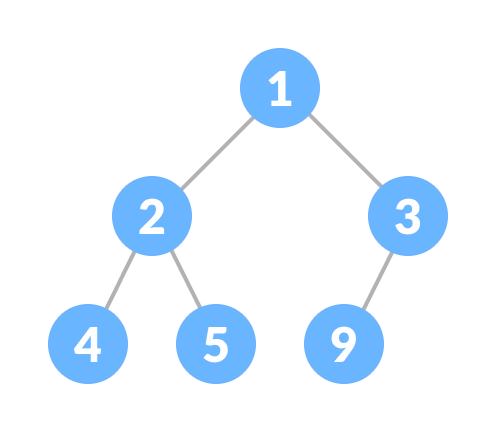
This type of data structure is also called a binary heap.
Some of the important operations performed on a heap are described below along with their algorithms.
Heapify is the process of creating a heap data structure from a binary tree. It is used to create a Min-Heap or a Max-Heap.




Algorithm
Heapify(array, size, i) set i as largest leftChild = 2i + 1 rightChild = 2i + 2 if leftChild > array[largest] set leftChildIndex as largest if rightChild > array[largest] set rightChildIndex as largest swap array[i] and array[largest]To create a Max-Heap:
MaxHeap(array, size) loop from the first index of non-leaf node down to zero call heapifyFor Min-Heap, both leftChild and rightChild must be larger than the parent for all nodes.
Algorithm for insertion in Max Heap
If there is no node, create a newNode. else (a node is already present) insert the newNode at the end (last node from left to right.) heapify the array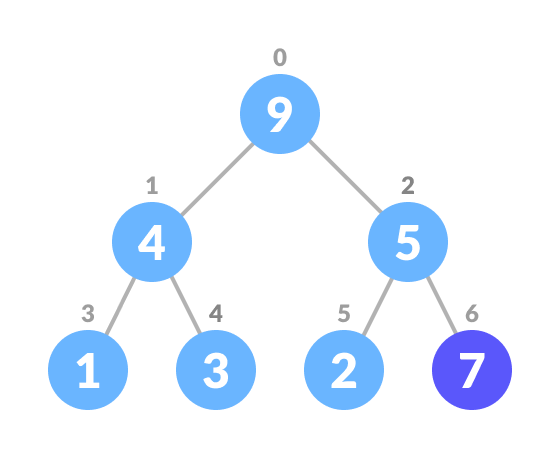
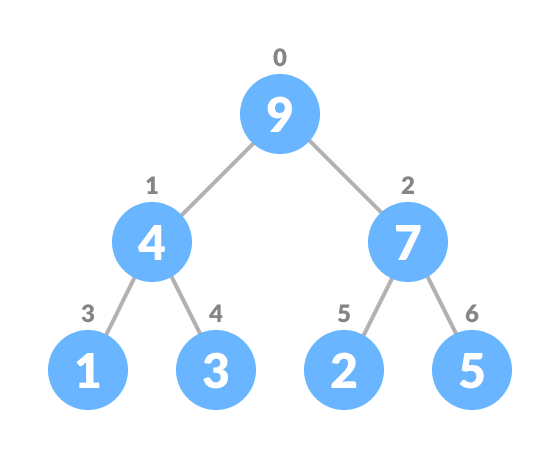
For Min Heap, the above algorithm is modified so that parentNode is always smaller than newNode .
Algorithm for deletion in Max Heap
If nodeToBeDeleted is the leafNode remove the node Else swap nodeToBeDeleted with the lastLeafNode remove noteToBeDeleted heapify the array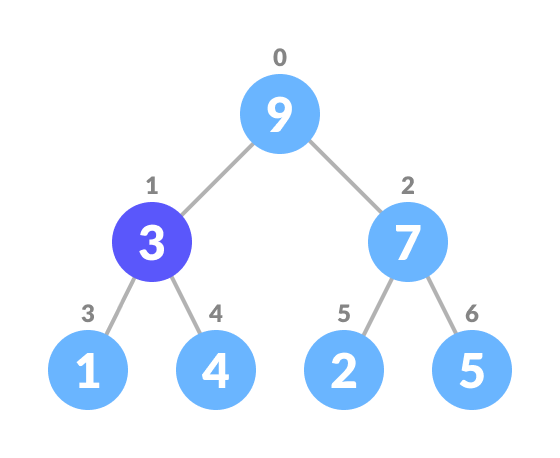
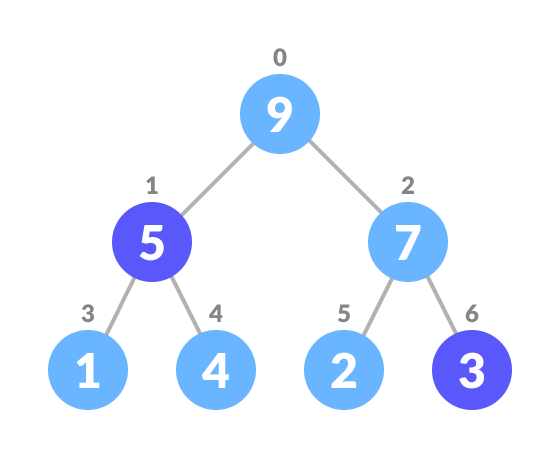
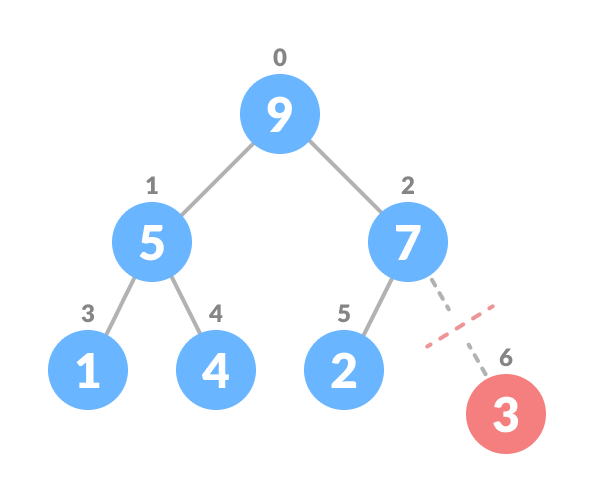
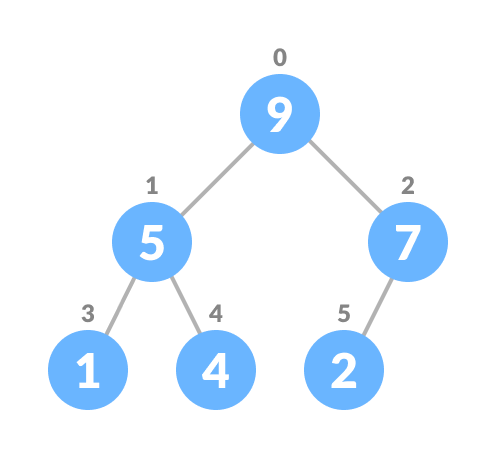
For Min Heap, above algorithm is modified so that both childNodes are greater smaller than currentNode .
Peek operation returns the maximum element from Max Heap or minimum element from Min Heap without deleting the node.
For both Max heap and Min Heap
return rootNode
Extract-Max returns the node with maximum value after removing it from a Max Heap whereas Extract-Min returns the node with minimum after removing it from Min Heap.
# Max-Heap data structure in Python def heapify(arr, n, i): largest = i l = 2 * i + 1 r = 2 * i + 2 if l < n and arr[l] >arr[largest]: largest = l if r < n and arr[r] >arr[largest]: largest = r if largest != i: arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i] heapify(arr, n, largest) def insert(array, newNum): array.append(newNum) current = len(array) - 1 while current > 0: parent = (current - 1) // 2 if array[current] > array[parent]: array[current], array[parent] = array[parent], array[current] current = parent else: break def deleteNode(array, num): size = len(array) i = 0 for i in range(size): if array[i] == num: break # Swap with the last element array[i], array[-1] = array[-1], array[i] array.pop() # Remove the last element which is now the number to be deleted # Only run heapify if the deleted node was not the last node if i < len(array): heapify(array, len(array), i) arr = [] insert(arr, 3) insert(arr, 4) insert(arr, 9) insert(arr, 5) insert(arr, 2) print("Max-Heap array:", arr) deleteNode(arr, 4) print("After deleting an element:", arr) // Max-Heap data structure in Java import java.util.ArrayList; class Heap < void heapify(ArrayListhT, int i) < int size = hT.size(); int largest = i; int l = 2 * i + 1; int r = 2 * i + 2; if (l < size && hT.get(l) >hT.get(largest)) largest = l; if (r < size && hT.get(r) >hT.get(largest)) largest = r; if (largest != i) < int temp = hT.get(largest); hT.set(largest, hT.get(i)); hT.set(i, temp); heapify(hT, largest); >> void insert(ArrayList hT, int newNum) < int size = hT.size(); if (size == 0) < hT.add(newNum); >else < hT.add(newNum); for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) < heapify(hT, i); >> > void deleteNode(ArrayList hT, int num) < int size = hT.size(); int i; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) < if (num == hT.get(i)) break; >int temp = hT.get(i); hT.set(i, hT.get(size-1)); hT.set(size-1, temp); hT.remove(size-1); for (int j = size / 2 - 1; j >= 0; j--) < heapify(hT, j); >> void printArray(ArrayList array, int size) < for (Integer i : array) < System.out.print(i + " "); >System.out.println(); > public static void main(String args[]) < ArrayListarray = new ArrayList(); int size = array.size(); Heap h = new Heap(); h.insert(array, 3); h.insert(array, 4); h.insert(array, 9); h.insert(array, 5); h.insert(array, 2); System.out.println("Max-Heap array: "); h.printArray(array, size); h.deleteNode(array, 4); System.out.println("After deleting an element: "); h.printArray(array, size); > >// Max-Heap data structure in C #include int size = 0; void swap(int *a, int *b) < int temp = *a; *a = *b; *b = temp; >void heapify(int array[], int size, int i) < int largest = i; int l = 2 * i + 1; int r = 2 * i + 2; if (l < size && array[l] >array[largest]) largest = l; if (r < size && array[r] >array[largest]) largest = r; if (largest != i) < swap(&array[i], &array[largest]); heapify(array, size, largest); >> void insert(int array[], int newNum) < array[size] = newNum; size += 1; int current = size - 1; while (current != 0) < int parent = (current - 1) / 2; if (array[current] >array[parent]) < swap(&array[current], &array[parent]); current = parent; >else < break; >> > void deleteRoot(int array[], int num) < int i; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) < if (array[i] == num) break; >swap(&array[i], &array[size - 1]); // Reduce the size of the heap since the last element is now removed size -= 1; // Heapify from the current index to adjust the rest of the heap if (i < size) < heapify(array, size, i); >> void printArray(int array[], int size) < for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) printf("%d ", array[i]); printf("\n"); >int main()
// Max-Heap data structure in C++ #include #include using namespace std; void swap(int *a, int *b) < int temp = *a; *a = *b; *b = temp; >void heapify(vector &hT, int i) < int size = hT.size(); int largest = i; int l = 2 * i + 1; int r = 2 * i + 2; if (l < size && hT[l] >hT[largest]) largest = l; if (r < size && hT[r] >hT[largest]) largest = r; if (largest != i) < swap(&hT[i], &hT[largest]); heapify(hT, largest); >> void insert(vector &hT, int newNum) < hT.push_back(newNum); int current = hT.size() - 1; // Bubble up while (current >0) < int parent = (current - 1) / 2; if (hT[current] >hT[parent]) < swap(&hT[current], &hT[parent]); current = parent; >else < break; >> > void deleteNode(vector &hT, int num) < int size = hT.size(); int i; for (i = 0; i < size; i++) < if (num == hT[i]) break; >swap(&hT[i], &hT[size - 1]); hT.pop_back(); // Update size after popping size = hT.size(); // Heapify from the current index to adjust the rest of the heap if (i < size) < heapify(hT, i); >> void printArray(const vector &hT) < for (int num : hT) cout int main() < vectorheapTree; insert(heapTree, 3); insert(heapTree, 4); insert(heapTree, 9); insert(heapTree, 5); insert(heapTree, 2); cout